Vue2 源码从零详解系列文章, 还没有看过的同学可能需要看一下之前的,vue.windliang.wang/ (opens new window)
# 场景1
在 Vue2剥丝抽茧-响应式系统之watch (opens new window) 中,我们实现了 initWatch ,对于下边的代码
import { observe } from "./reactive";
import { initWatch } from "./state";
const options = {
data: {
title: "liang",
},
watch: {
title(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log("收到变化", newVal, oldVal);
},
},
};
observe(options.data);
initWatch(options.data, options.watch);
options.data.title = "changeTitle";
我们可以感知到 title 的变化,但 title 赋初始值的时候并不会感知到,Vue 中我们可以通过添加 immediate 属性来达到。
import { observe } from "./reactive";
import { initWatch } from "./state";
const options = {
data: {
title: "liang",
},
watch: {
title: {
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log("收到变化", newVal, oldVal);
},
immediate: true,
},
},
};
observe(options.data);
initWatch(options.data, options.watch);
options.data.title = "changeTitle";
回调函数是传递一个 handler 方法。
接下来我们来实现一下。
# 实现思路
其实思路非常简单,实现两点就可以:
- 解析
handler,将传入的handler和options分开 - 如果
immediate为true,立即执行一次回调函数
可以直接看代码了:
/**
* Get the raw type string of a value, e.g., [object Object].
*/
const _toString = Object.prototype.toString;
/**
* Strict object type check. Only returns true
* for plain JavaScript objects.
*/
export function isPlainObject(obj) {
return _toString.call(obj) === "[object Object]";
}
function createWatcher(data, expOrFn, handler, options) {
// 如果是对象,就将 handler 和 options 分离
if (isPlainObject(handler)) {
options = handler;
handler = handler.handler;
}
return $watch(data, expOrFn, handler, options);
}
立即执行回调函数:
function $watch(data, expOrFn, handler, options) {
const watcher = new Watcher(data, expOrFn, handler);
/******新增 *************************/
if (options.immediate) {
handler.call(data, watcher.value);
}
/************************************/
}
# 测试
回到开头的代码:
import { observe } from "./reactive";
import { initWatch } from "./state";
const options = {
data: {
title: "liang",
},
watch: {
title(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log("收到变化", newVal, oldVal);
},
},
};
observe(options.data);
initWatch(options.data, options.watch);
options.data.title = "changeTitle";
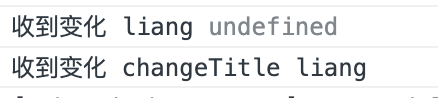
第一次得到初值的时候也会触发回调函数,只不过 oldVal 是 undefined 。
# 场景2
import { observe } from "./reactive";
import { initWatch } from "./state";
const options = {
data: {
info: {
name: {
firstName: "wind",
secondName: "liang",
},
},
},
watch: {
"info.name": {
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log("收到变化", newVal, oldVal);
},
},
},
};
observe(options.data);
initWatch(options.data, options.watch);
options.data.info.name = { // 整体赋值
firstName: "wind2",
secondName: "liang2",
};
setTimeout(() => {
options.data.info.name.firstName = "wind3"; // 单独赋值
}, 0);
当监听对象的时候,如果是对象 options.data.info.name 整体赋值,会调用回调函数。
但如果给对象中的属性单独赋值 options.data.info.name.firstName 就不会触发回调函数了。
(至于第二次赋值为什么放到了 setTimeout 中,可以回顾一下 Vue2剥丝抽茧-响应式系统之nextTick (opens new window)。)
为了监听到对象内部的变化,Vue 提供了 deep 属性供我们使用。
const options = {
data: {
info: {
name: {
firstName: "wind",
secondName: "liang",
},
},
},
watch: {
"info.name": {
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log("收到变化", newVal, oldVal);
},
deep: true,
},
},
};
接下来我们来实现 deep 的功能。
# 实现思路
我们只需要在收集 Watcher 的过程中,深度遍历一遍当前对象,触发所有属性的 get ,然后每一个属性就会收集到当前 Watcher ,这样改变对象内部的值的时候,就会触发该 Watcher ,从而执行回调函数。
遍历对象的话,首先就需要一个 travel 函数。
/* @flow */
import { isObject } from "./util";
const seenObjects = new Set();
/**
* Recursively traverse an object to evoke all converted
* getters, so that every nested property inside the object
* is collected as a "deep" dependency.
*/
export function traverse(val) {
_traverse(val, seenObjects);
seenObjects.clear();
}
function _traverse(val, seen) {
let i, keys;
const isA = Array.isArray(val);
if ((!isA && !isObject(val)) || Object.isFrozen(val)) {
return;
}
if (val.__ob__) {
const depId = val.__ob__.dep.id;
if (seen.has(depId)) {
return;
}
seen.add(depId);
}
// 判断是数组还是对象
if (isA) {
i = val.length;
while (i--) _traverse(val[i], seen);
} else {
keys = Object.keys(val);
i = keys.length;
// 遍历对象的每一个 key
while (i--) _traverse(val[keys[i]], seen);
}
}
两个循环比较好理解,增加了seen 变量来去重是为了防止对象之间的循环引用,造成死循环。
const obj1 = {}
const obj2 = {}
obj1.data = obj2
obj2.data = obj1
const data = {
obj1,
obj2,
}
当我们遍历 obj1 的时候会遍历 obj2 ,遍历 obj2 的时候又会遍历 obj1 ,从而造成死循环。
有了 travel 函数以后,剩下的就水到渠成了。
首先在 Watcher 的构造函数中保存 deep 的值。
export default class Watcher {
constructor(data, expOrFn, cb, options) {
this.data = data;
if (typeof expOrFn === "function") {
this.getter = expOrFn;
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn);
}
this.depIds = new Set(); // 拥有 has 函数可以判断是否存在某个 id
this.deps = [];
this.newDeps = []; // 记录新一次的依赖
this.newDepIds = new Set();
this.id = ++uid; // uid for batching
this.cb = cb;
// options
if (options) {
/******新增 *************************/
this.deep = !!options.deep;
/************************************/
this.sync = !!options.sync;
}
this.value = this.get();
}
...
}
然后在执行当前 Watcher 的时候深度遍历对象的所有属性。
/**
* Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies.
*/
get() {
pushTarget(this); // 保存包装了当前正在执行的函数的 Watcher
let value;
try {
value = this.getter.call(this.data, this.data);
} catch (e) {
throw e;
} finally {
/******新增 *************************/
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value);
}
/************************************/
popTarget();
this.cleanupDeps();
}
return value;
}
在 $watch 方法中把 options 传递给 Watcher 。
function $watch(data, expOrFn, handler, options) {
/******新增 options*************************/
const watcher = new Watcher(data, expOrFn, handler, options);
/************************************/
if (options.immediate) {
handler.call(data, watcher.value);
}
return function unwatchFn() {
watcher.teardown();
};
}
# 测试
import { observe } from "./reactive";
import { initWatch } from "./state";
const options = {
data: {
info: {
name: {
firstName: "wind",
secondName: "liang",
},
},
},
watch: {
"info.name": {
handler(newVal, oldVal) {
console.log("收到变化", newVal, oldVal);
},
deep: true,
},
},
};
observe(options.data);
initWatch(options.data, options.watch);
options.data.info.name = {
firstName: "wind2",
secondName: "liang2",
};
setTimeout(() => {
options.data.info.name.firstName = "wind3";
}, 0);
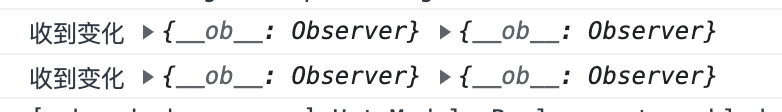
这样的话两次修改就都会触发 Watcher 的更新了。
# 总结
实现了 watch 中常用的 immediate 和 deep 。